I don’t have time for a real blog post, but here’s a quickie
in an attempt to keep this blog alive.
Dave Altig and Mike Bryan of the Atlanta Fed’s Macroblog
argue here that it wouldn’t make much difference if the Fed
were doing price level targeting (in which the future target path stays fixed
even when you miss a target, so you need catch-up inflation or catch-up
disinflation) rather than inflation targeting.
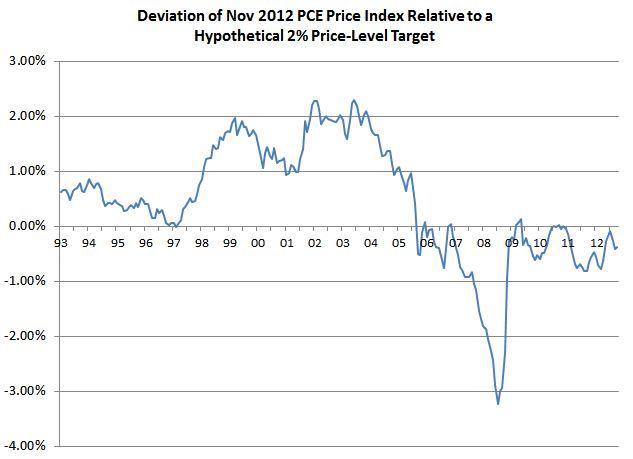
Their evidence is mostly from a chart like this (my replication using
monthly data, which you can confirm looks fairly similar to theirs which
appears to use annual data):
Quoting from their blog post:
Consider the first point on
the graph, corresponding to the year 1993….This point on the graph answers the
following question:
By what percent would the actual level of the personal consumption expenditure price index differ from a price-level target that grew by 2 percent per year beginning in 1993?
The succeeding points in the
chart answer that same question for the years 1994 through 2009.
In my case, as I said, it’s
monthly, and it goes all the way to 2012, but the idea is the same.
OK, fine. So here it looks like a price level target
would have produced roughly the same results as the Fed’s (unofficial until
January 2012) inflation target, and whether it would have undershot or overshot
depends on when you start the target path.
In particular, people who argue that we are undershooting right now
don’t seem to have much of an argument unless they start the target path in
2008 or later.
BUT…
The problem with this chart is that
it uses the headline PCE price index, whereas during most of this time (until
January 2012 when the official inflation targeting policy was introduced), the
Fed was perceived to be targeting core
PCE inflation (excluding food and energy, that is), not headline
inflation. Price-setters were making
their decisions largely under that assumption.
It makes no sense to go back to 1993 and set up a target path using the
headline price index when that index was irrelevant to the policy that the Fed
seemed to be following at the time.
Moreover, targeting the price level
using the headline price index is a bad idea anyhow. If you're going to use a price level
target (and I do think it would be better than an inflation target), then you
don't want to use a price index that will be subject to shocks that are
volatile but persistent. A one-time increase in the price of oil should not
require a subsequent compensating decline in other prices to offset it (nor
should a one-time decrease in the price of oil require a subsequent burst of
inflation to offset it). Theoretical arguments would suggest using an index of sticky
prices, but the core is a reasonable approximation.
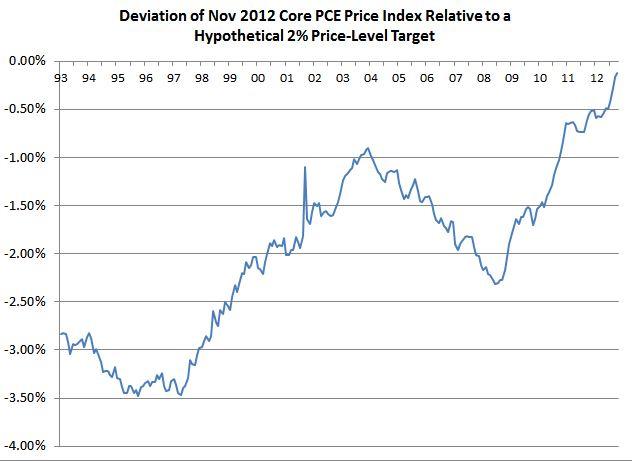
Here’s what my chart above looks
like when you use the core PCE price index instead of the headline index.
Very different. By this measure we are undershooting now no
matter when you start the target path.
And unless you cherry-pick the starting point in 2003 or 2011, the size
of the undershoot is not insignificant.
If you compare to the 1990’s, the Fed was already slightly behind when
the Great Recession began, and they have fallen further and further behind
since then. Price level targeting, using
the core price index, would require the Fed to promise a significant amount of
catch-up inflation in the coming years.
DISCLOSURE: Through my investment
and management role in a Treasury directional pooled investment vehicle and
through my role as Chief Economist at Atlantic Asset Management, which
generally manages fixed income portfolios for its clients, I have direct or
indirect interests in various fixed income instruments, which may be impacted
by the issues discussed herein. The views expressed herein are entirely my own
opinions and may not represent the views of Atlantic Asset Management. This
article should not be construed as investment advice, and is not an offer to
participate in any investment strategy or product.